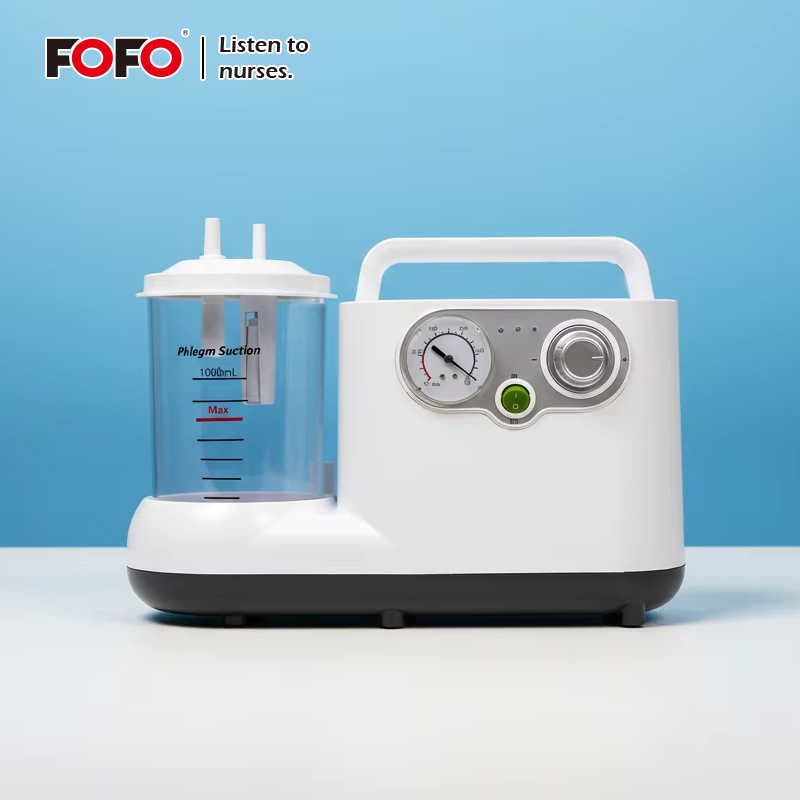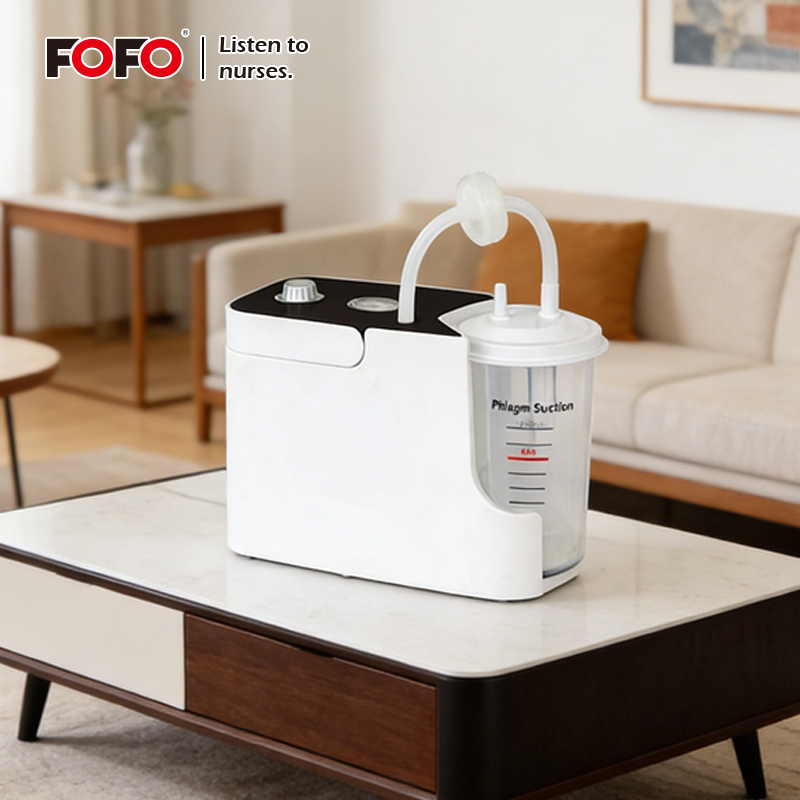
In the realm of modern healthcare and emergency response, suction machines play a pivotal role in maintaining patient safety and comfort. These essential medical devices are designed to clear the airway of blood, saliva, vomit, or other secretions to allow for proper breathing. Beyond their critical use in hospitals, they are also indispensable in home healthcare settings, ambulatory services, and surgical centers. This comprehensive guide explores the types, components, applications, safety protocols, maintenance requirements, and selection criteria of suction machines, equipping medical professionals and caregivers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
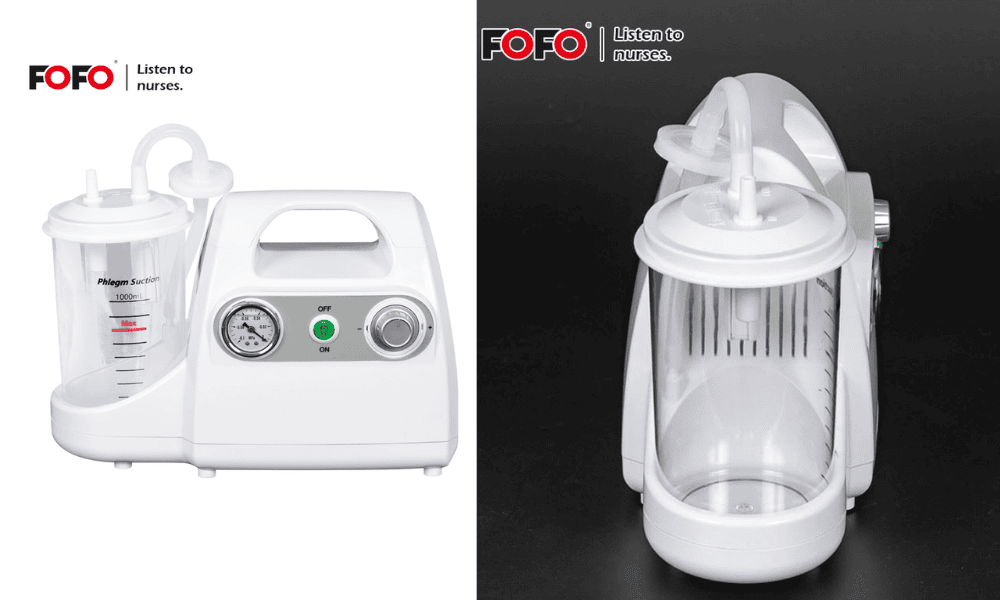

Phlegm Suction Machine Medical
Contents
Understanding the Different Types of Suction machines
There are various suction machines designed to serve specific clinical needs and environments. Broadly, they can be categorized into manual, electric, and battery-operated models. Manual suction devices are typically used in emergency or field settings due to their portability and independence from electricity. They are hand or foot operated and best suited for short-term, low-volume suctioning needs.
Electric suction machines, commonly found in hospitals and clinics, offer higher suction power and can handle continuous operation. These are typically plugged into a wall outlet and are ideal for surgical procedures, intensive care units (ICUs), and postoperative recovery rooms.
Battery-operated models provide the convenience of portability while maintaining adequate suction strength. These devices are crucial in ambulatory services and home healthcare, where mobility and reliability are essential. Portable suction machines often include rechargeable batteries and lightweight designs for easy transport, making them a practical choice for home caregivers and paramedics alike.
Core Components and Operating Principles
At the heart of all suction machines are a few critical components that ensure functionality and efficiency. These include the vacuum pump, collection canister, suction tubing, pressure gauge, and power supply. The vacuum pump creates the negative pressure needed to extract fluids from the patient’s airway or surgical site.
Fluids are collected in a canister that is often fitted with a hydrophobic filter to prevent overflow and contamination. The tubing connects the patient to the device and must be sterile and disposable to prevent infections. A pressure gauge allows clinicians to monitor and adjust suction levels according to the patient’s needs and procedural requirements.
The principle of operation involves creating a vacuum that lowers the air pressure inside the tubing. This difference in pressure pulls fluids through the tube into the collection canister. Effective suction machines maintain consistent pressure, are quiet in operation, and are designed for minimal user intervention during critical moments.
Clinical Applications and Indications
Suction machines are used across a wide range of clinical scenarios. In emergency medicine, they are critical for clearing blocked airways caused by trauma, drowning, or cardiac arrest. Suctioning ensures that paramedics and ER personnel can maintain a patent airway before intubation or while waiting for further medical intervention.
In surgical environments, suction machines are used to remove blood and other bodily fluids from the operative field, maintaining visibility for the surgical team. Intensive care units frequently rely on suctioning to prevent the accumulation of mucus and secretions in patients who are intubated or mechanically ventilated.
Home healthcare also benefits from suction machines, especially for patients with chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, ALS, or neuromuscular disorders. Regular suctioning at home can prevent complications like pneumonia and reduce hospital readmissions. Pediatric care also utilizes suction devices, especially in cases involving infants with swallowing difficulties or congenital anomalies that compromise normal breathing.
Safety Protocols and Best Practice Guidelines
The use of suction machines demands strict adherence to safety protocols to protect both patients and healthcare providers. Before using the machine, it is essential to inspect the device for damage or contamination, ensure proper assembly, and test the suction pressure. All tubing and collection containers must be sterile and replaced after each use.
Operators must monitor patient vitals during suctioning, including oxygen saturation and heart rate, to avoid complications like hypoxia or bradycardia. Suctioning should be limited in duration, ideally under 15 seconds per attempt, with adequate recovery time between attempts.
Proper PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) such as gloves, masks, and eye protection should always be worn when operating suction machines to prevent exposure to bodily fluids. All healthcare professionals must be thoroughly trained in using the specific model at their facility, including emergency procedures in case of equipment failure.
Maintenance, Cleaning, and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance is vital for the optimal performance and longevity of suction machines. After each use, all disposable parts such as suction tubing and collection canisters should be discarded appropriately. Reusable parts must be cleaned with disinfectants that are compatible with medical-grade equipment.
Weekly or monthly checks should include inspecting the vacuum pump, checking for leaks, and verifying that the battery holds a full charge in portable models. Filters should be replaced regularly as clogged filters can compromise suction performance and pose infection risks.
Common issues with suction machines include reduced suction power, noisy operation, and error codes. Reduced suction might result from blocked tubing, a full canister, or motor malfunction. In such cases, step-by-step troubleshooting guidelines provided in the machine’s manual should be followed. For battery-operated models, battery calibration and replacement are crucial to avoid unexpected power loss during use.
Choosing the Right Suction Machine for Your Setting
Selecting the appropriate suction machine depends on the specific clinical setting, frequency of use, patient population, and mobility requirements. For hospital ICUs or operating rooms, a high-powered stationary electric suction machine with multiple suction ports and adjustable pressure settings is ideal.
For ambulatory services or home care, portable models that are lightweight, battery-operated, and easy to clean offer the best balance between functionality and convenience. Pediatric models are specially designed with lower suction pressure settings to prevent mucosal damage.
It is also important to consider the noise level of the device, especially in environments where patient comfort and rest are priorities. Some modern suction machines are designed with sound-dampening features to ensure quiet operation.
Additionally, always verify that the device complies with local and international medical standards, including ISO and CE certifications. Reliable manufacturers often offer extended warranties, training support, and readily available replacement parts—factors that significantly enhance the device’s usability and service life.
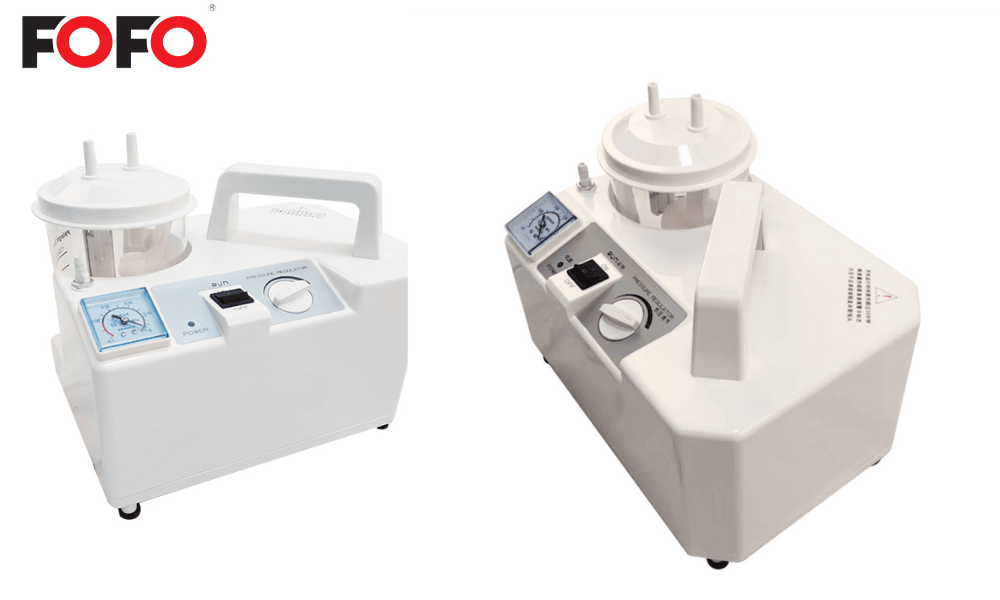
Custom Portable Phlegm Suction Machine
Suction machines are more than just tools for airway management—they are vital components of modern medical care across diverse healthcare settings. From emergency medicine to long-term home care, these devices save lives and contribute significantly to patient recovery and comfort. Understanding the types of suction machines, their internal mechanisms, proper applications, and safety guidelines is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers alike.
By maintaining regular cleaning and conducting prompt troubleshooting, the operational efficiency and hygiene of these machines can be preserved. More importantly, selecting the right model tailored to your specific environment ensures optimal outcomes for patients and ease of use for practitioners.
As healthcare continues to evolve, so too do suction machines, becoming quieter, more efficient, and easier to manage. Their role in critical care will only expand, making it more important than ever to stay informed, trained, and equipped with the most suitable equipment. Whether in a bustling hospital or a quiet home, suction machines remain silent yet powerful allies in the pursuit of better patient care.For example: “Want to learn more about suction machines? Contact us now to get a quote!”
Previous News
A Simple Tilt Accelerates Recovery—Rehab Specia...Next News
Hand Recovery Revolution Restores Post Stroke F...Feature Product
-
Portable Electric Sputum Suction Machine FO9001-D
Portable Electric Sputum Suction Machine ...
-
Phlegm Suction Machine – Electric & ...
Electric Surgical Portable Phlegm Suction...
-
Portable Compressor Nebulizer – Dog Design BC68...
Portable Compressor Nebulizer – Dog Design: A L...



